11 Stages To Become A JavaScript Full-Stack Engineer
Kickstart Your Career And Become A JavaScript Full-Stack Developer
Last year I created a list to kickstart your career and become a Full-Stack developer. I realized that they are still valid and want to share them here!
Paul Knulst in Programming • 7 min read
Last year, I have received multiple messages, mostly from newcomers that have just graduated and stepped into the world of coding. Most of the questions asked are about how to quickly improve their skills, how to become a Full Stack Developer, or how to choose a career direction.
While I try replying to everyone by one, I want to combine my own experiences and created a roadmap on how to become a Full-Stack Engineer that I want to share with everyone.
Stage 1 - HTML
Before starting with any programming language you should learn basic HTML. A good start will be the tutorial of W3Schools that teaches all the basics and also some advanced information: find it here
Stage 2 - CSS (Grid, Flex)
With knowledge about HTML, you should learn about CSS to style your website. Again, W3Schools provides a good tutorial: find it here
Stage 3 - JavaScript + DOM
Now it's time to learn JavaScript. JavaScript is one of the most used programming languages all over the world. To learn it you can use another W3Schools tutorial.
Also, I have written an article to learn advanced JavaScript with Gamification.
Stage 4 - Node.js
Node.js is a powerful JavaScript-based platform that is built on Google Chrome’s JavaScript V8 Engine and provides an event-driven, non-blocking (asynchronous) I/O and cross-platform runtime environment for building highly scalable server-side applications using JavaScript.
Start by downloading and installing the latest Node version for your OS on nodejs.dev. This is mandatory for further progression as a JavaScript (TypeScript) developer.
Afterward, you should check out their introduction to learn some basics about Node.js.
Before heading to the next stage you should make yourself familiar with the npm ecosystem. Consider answering these questions before starting with React:
What is NPM?
How can I install something?
What is a package.json
I need package XX what should I do?
Stage 5 - React
If you are proficient with JavaScript (and maybe TypeScript) you should learn React because it is the most used framework based on data from npmtrends.com:
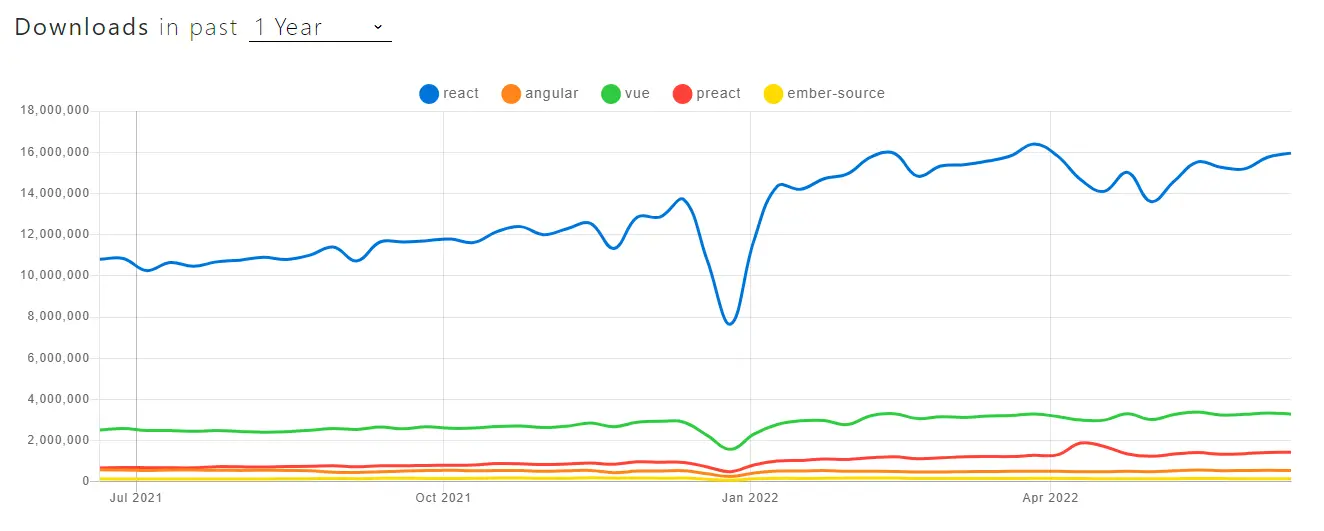
Remember: Mastering React takes some time because it has many different concepts that all become important during development.
My personal advice would be to work on the three following lists step by step before continuing to MySQL:
Basics
How To Set Up Your DevEnv
JSX
Components
State
Props
Lists/Keys
Lifecycle Methods
Advanced React Concepts
Styling
Form Handling
Data Handling
Reconciliation Process
Hooks
Custom Hooks
Context
Mastering React
Lazy Loading
Portals
State Management
Routing
Theming
Patterns
Anti-Patterns
This article from me here on dev.to has also come links for becoming a React developer
Stage 6 - MySQL
After you mastered JavaScript and React to create beautiful websites the next step will be to use persistent data within these websites. Often, this is done by connecting to a database like MySQL, PostgreSQL, or SQLite.
For simplicity, you should learn MySQL over PostgreSQL!
As a developer, you have to be familiar with MySQL because it is ideal for both small and large applications (PostgreSQL is an advancement in DBMS but MySQL is basic knowledge).
To learn MySQL you can use a W3School Tutorial which will teach you all the basics to understand every MySQL query you will encounter in different applications.
One important thing is, that you have to understand database design more than queries because in future stages you will use a technique (ORM) that helps you with queries anyway. For this, you have to understand Database Normalization. This is very important if you want to work with relational databases!
Stage 7 - MongoDB
In contrast to MySQL, MongoDB is a document-oriented database classified as NoSQL. It uses JSON-like documents with optional schemas to store data.
Get familiar with NoSQL database design and read and understand this.
Stage 8 - The CRUD Pattern
If you are working with persistent data it is mandatory that you understand the CRUD pattern. CRUD stands for Create, Read, Update, Delete and describes the four basic operations for persistent data.
It should be sufficient to read about it on Wikipedia.
Stage 9 — ORM And ODM
ORM stands for Object-Relational Mapping; ODM stands for Object Document Mapper. Both are techniques that are used to query and manipulate data from a database using an object-oriented paradigm.
Often, when developers talk about ORM or ODM they refer to a library that implements any (or both) of these techniques.
You should learn at least one of the following supporting both Database technologies:
TypeOrm (SQL and NoSQL)
Prisma (SQL and MongoDB)
Mongoose (only MongoDB)
Typegoose (Mongoose for TypeScript)
Knex.js (SQL)
sequelize (SQL)
Personally, I would recommend learning TypeOrm AND Prisma!
Stage 10 - Build Side Projects To Gain Experience
Now that you know a programming language, a framework, and how to use a database you can start creating some projects.
This stage is very important in becoming a full-stack developer because you never encounter real-life problems in tutorials that you will face while working on your own project.
Here are some ideas for cool projects:
Goal Tracking App
Simple app that tracks your personal goals. Save goals in a database and show them in a nice way in the front end.
Clone A Website
Search for a nice website and try to clone it. Copy the contents and try to extrapolate the functions that the website uses. Then try to implement it for your own website.
Developer Portfolio
A very important project that you should create is a portfolio. A Portfolio is an important website that will represent yourself. If you apply for a job you will have a nice-looking website that will show your skills or introduce yourself.
Get inspiration here:
Stage 11 - Deploy Your Side Project
The last stage is about deploying your project on a server. This stage is also mandatory because as a full-stack developer, you should know how to deploy your app in a production environment.
I would recommend learning about Docker and how it can be used to host different websites. As a starting point, you can check out an introduction from me to Docker here. If you are already into Docker you can check out this article where I explain how to deploy Traefik (a load balancer) that automatically creates SSL certificates for every service you will deploy on your server.
If you have read and understood both articles you can check out this article:
It describes how you can deploy a simple website in a Docker environment that already runs a Traefik.
Congratulations, you can call yourself a Full Stack developer!
Closing Notes
Hopefully, these resources will help you to become a Full Stack Developer.
Also, if you have any questions, ideas, or recommendations, please jot them down below. I try to answer them if possible.
Writing has always been my passion and it gives me pleasure to help and inspire people.
This article was originally published on my blog at https://www.paulsblog.dev/11-stages-to-become-a-javascript-full-stack-engineer/
Feel free to connect with me on my blog, Medium, LinkedIn, Twitter, and GitHub.
🙌 Support this content
If you like this content, please consider supporting me. You can share it on social media or buy me a coffee! Any support helps!
Furthermore, you can sign up for my newsletter to show your contribution to my content. See the contribute page for all (free or paid) ways to say thank you!
Thanks! 🥰
Photo by Caspar Camille Rubin / Unsplash

